Urban Computing and AI
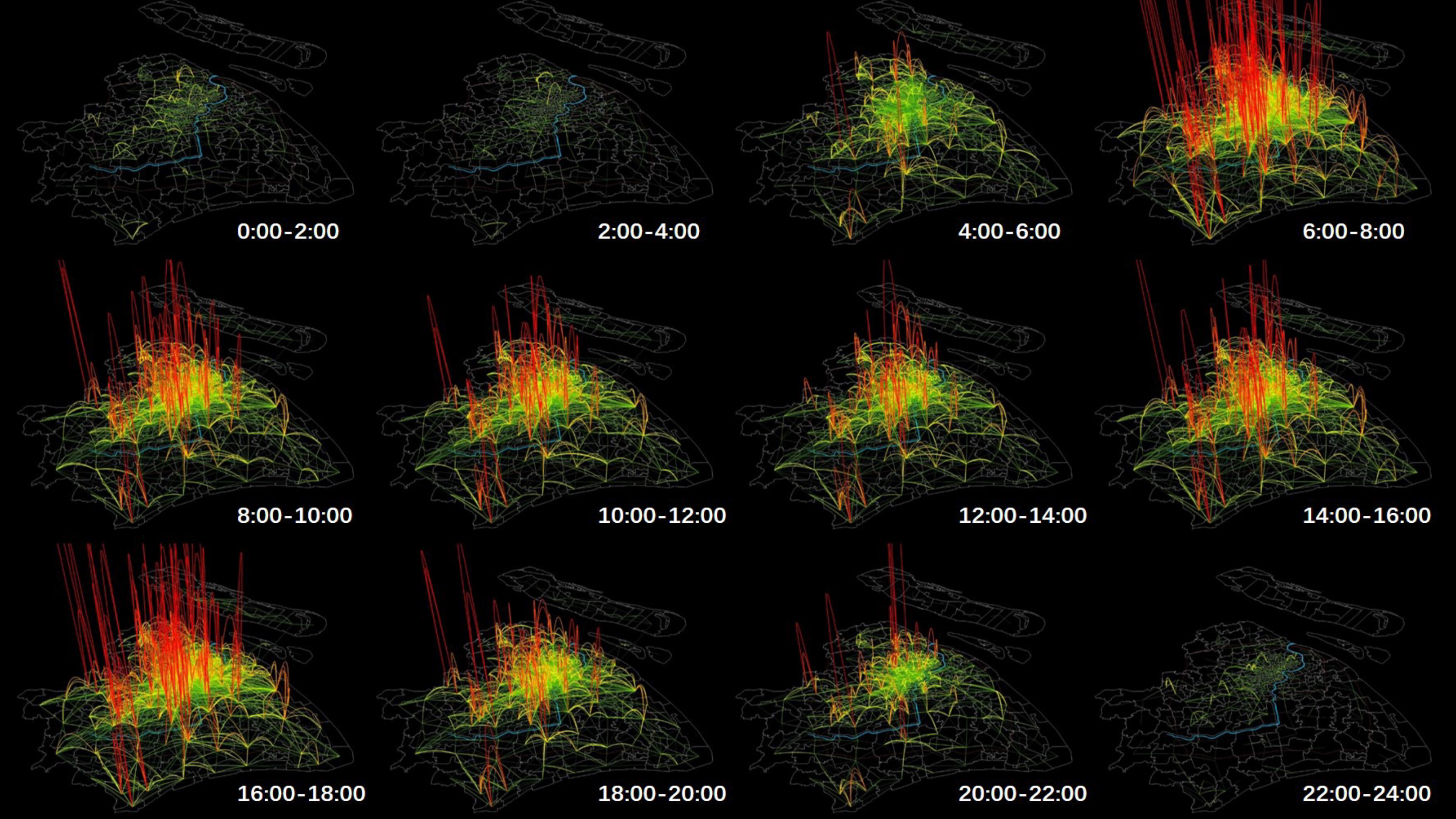
Human Mobility and Land Use Patterns
Land use functions can categorize places where people perform different socioeconomic activities. However, mobility patterns might vary significantly even within the same land use function as conventionally defined. This project explores land use subcategorization using mobile phone-derived human activities.
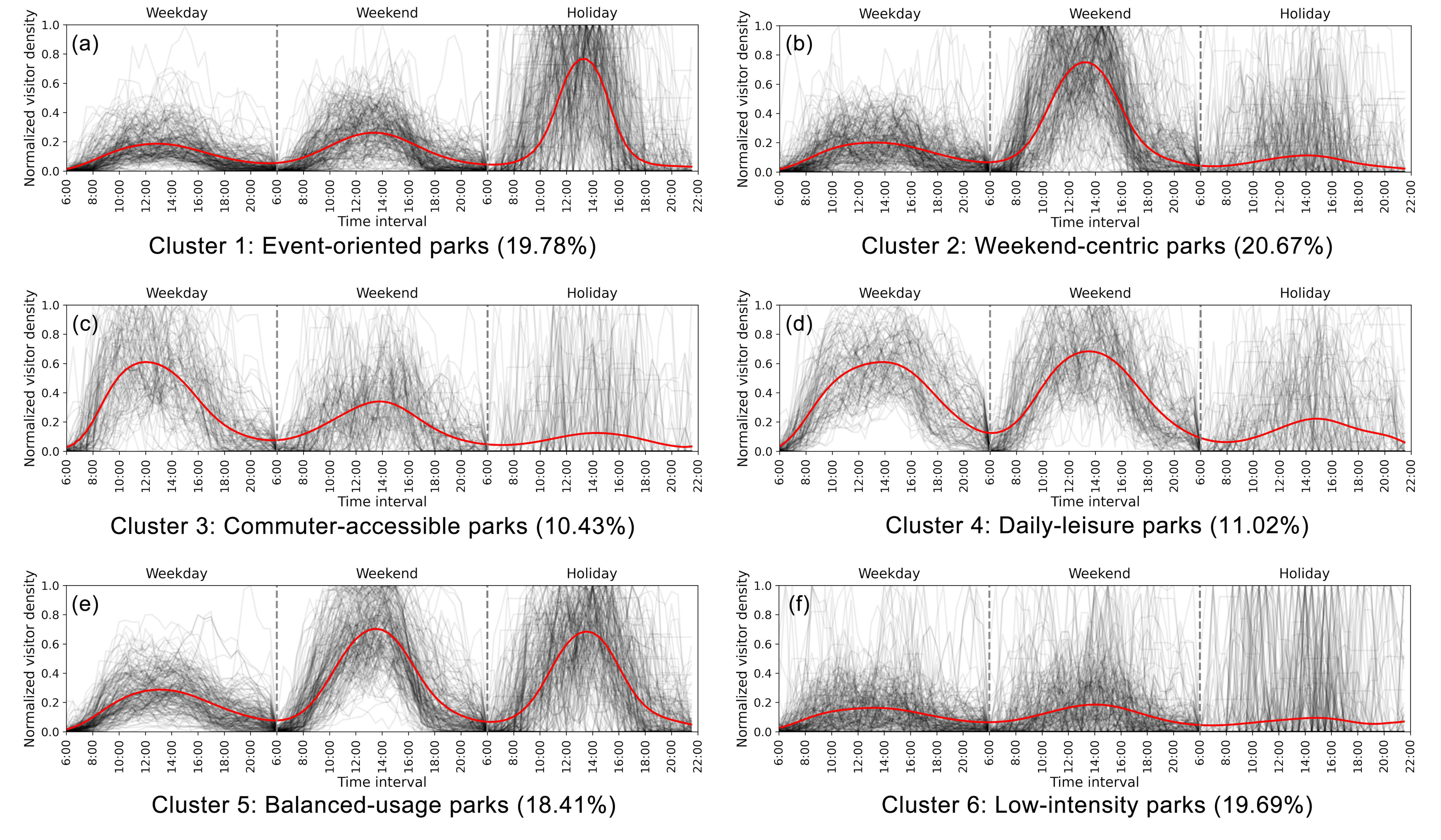
Planning for Rhythmized Urban Parks
This project proposes a paradigm shift in classifying, programming, and designing parks. Utilizing 1.5 million mobile phone records, we classified 254 urban parks in Tokyo based on their visitation patterns across different times of the day, week, and year.
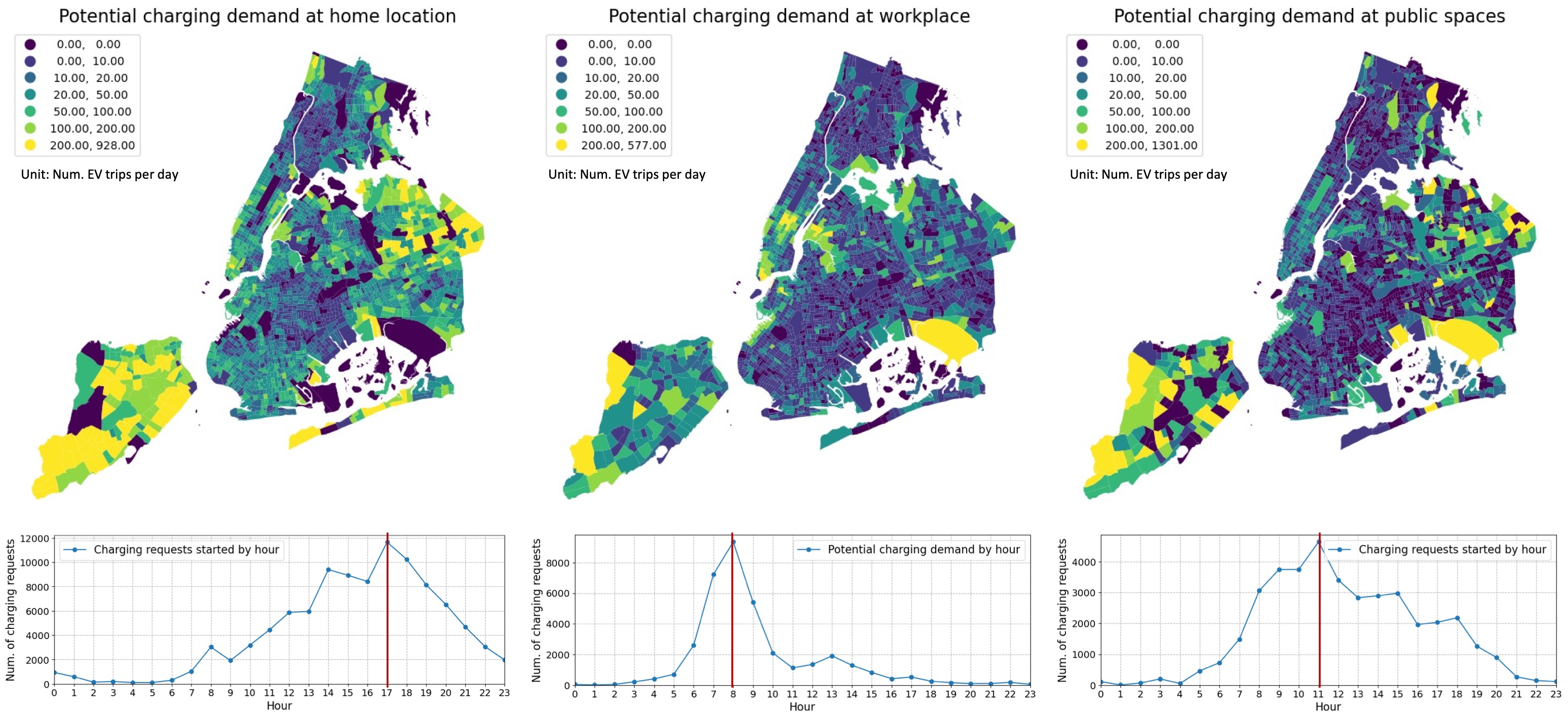
New York City Synthetic Electric Vehicles
This project uses National Household Travel Survey (NHTS) data, Atlas EV Registration data, and machine learning models to forecast EV ownership for a synthetic population. The proposed model predicts the number of EVs per zip code and assigns EVs to households.
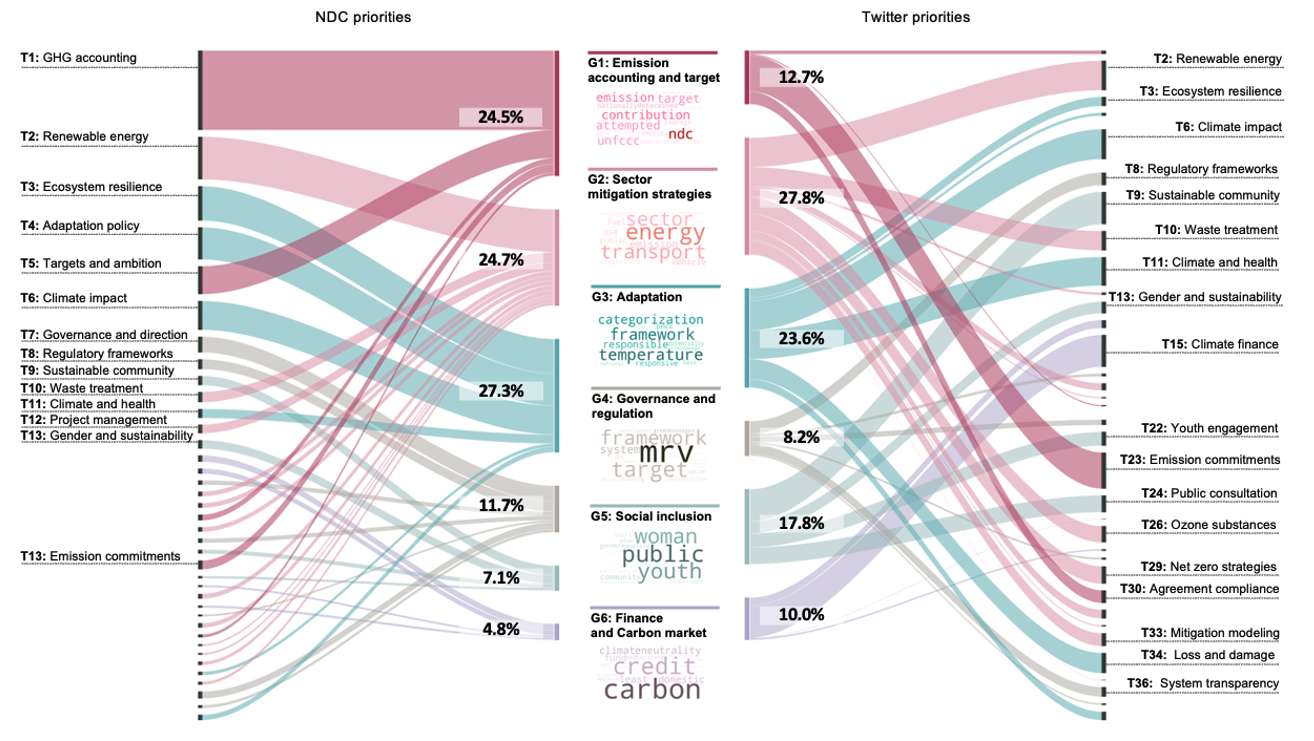
Detecting Climate Change Perception Gaps using LLMs
Our team integrated 195 Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) with approximately 400,000 climate-related Twitter posts from January to December 2022. We employed ClimateBERT to quantify global and city-level gaps between governmental action and public perception.
Choice Modeling with Large-scale Dataset
Agent-based Mixed Logit Model (AMXL)
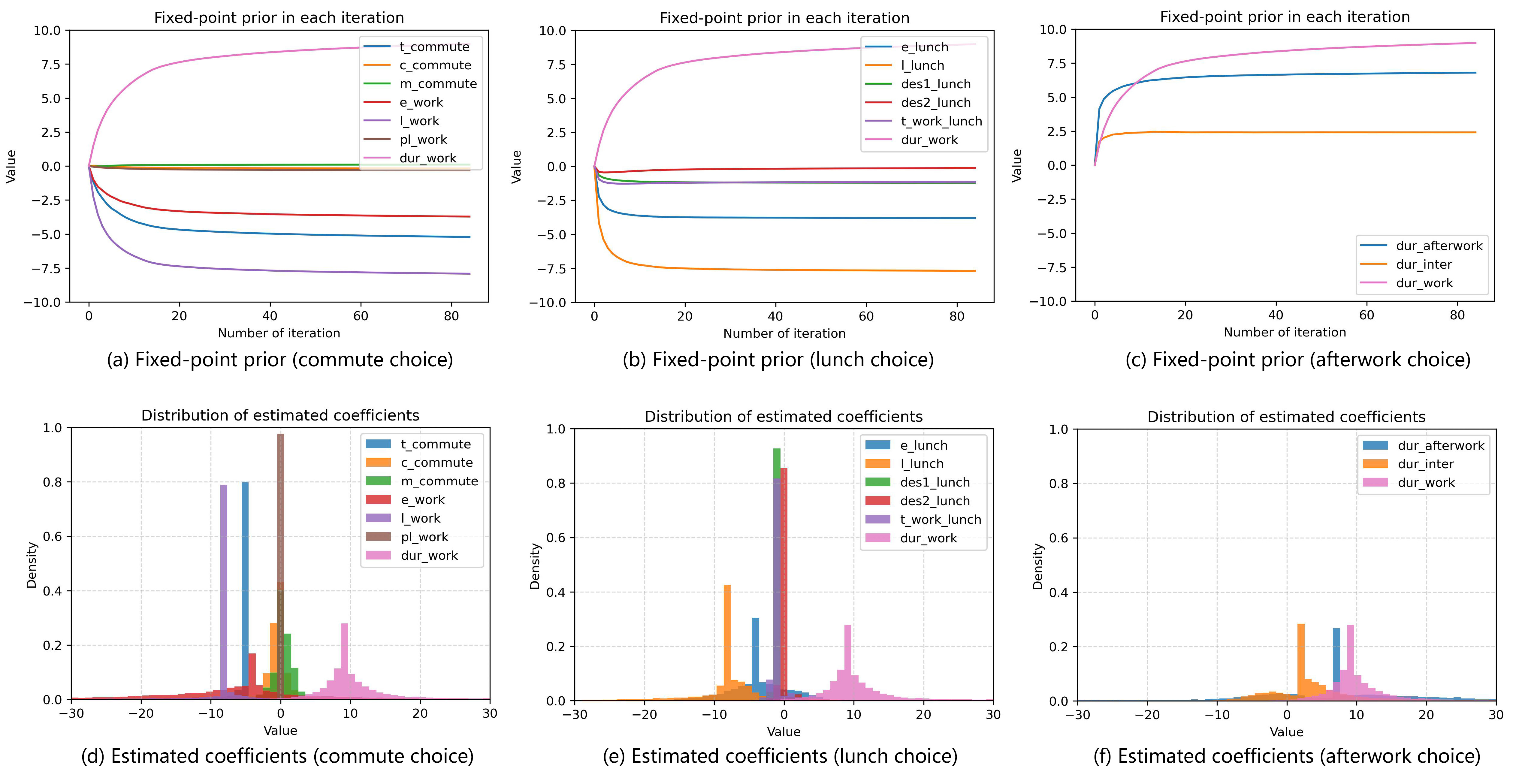
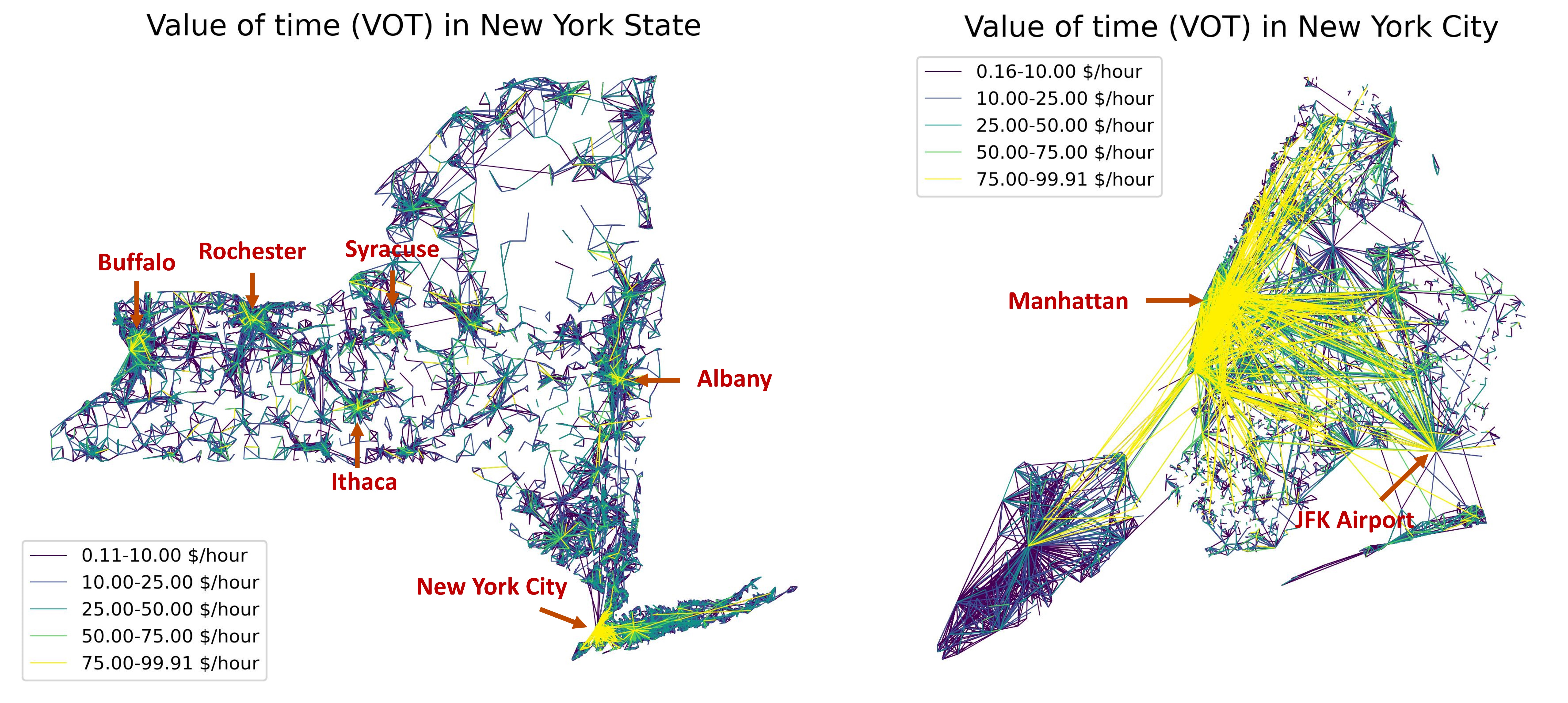
We propose an agent-based mixed-logit model (AMXL) that is estimated with inverse optimization (IO) estimation. The method provides joint, individual-specific, and deterministic estimation, which overcomes the limitations of discrete choice models (DCMs) given ubiquitous datasets.
Market-level Nonparametric Mixed Logit Model
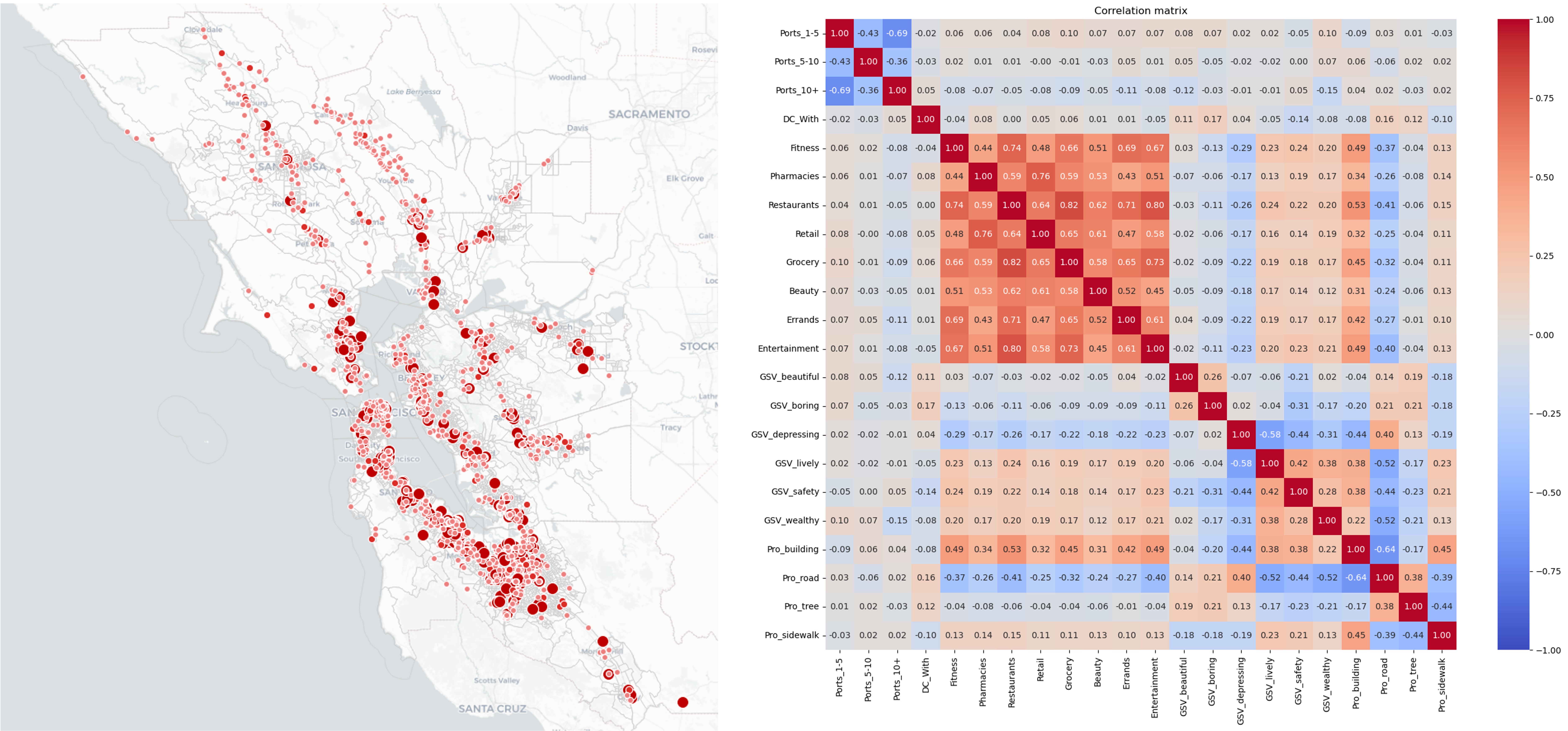
This project proposes a nonparametric mixed logit model that is estimated using market-level choice share data. The model treats each market as an agent and represents taste heterogeneity through market-specific parameters by solving a multiagent inverse utility maximization problem.
Modeling EV Charging Behavior using Individual Mobility Data
This NSF-SAI project focuses on an equitable and efficient allocation of EVCSs that benefits not only EV drivers but also supports the economic growth of the community. We leverage mobility phone data and apply AMXL to EV charging behavior modeling in Bay Area.
Equity-aware Transportation Logistics
Mobility Service Decision Support Tool
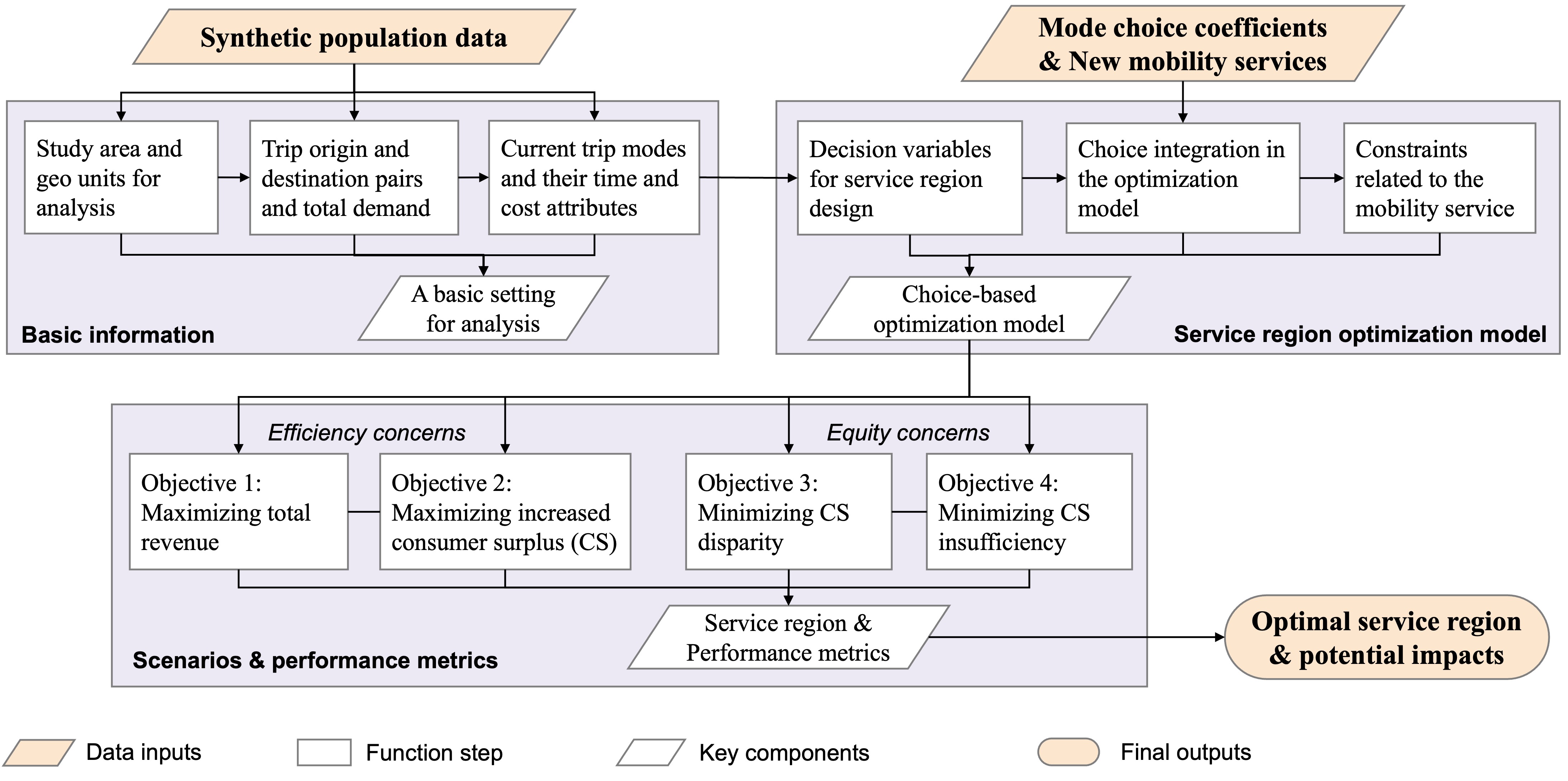
We integrate synthetic population data and a choice-based optimization model to support large-scale mobility service region design with equity concerns. We test using New York State synthetic data and illustrate its application by considering new ride-hailing and microtransit services.
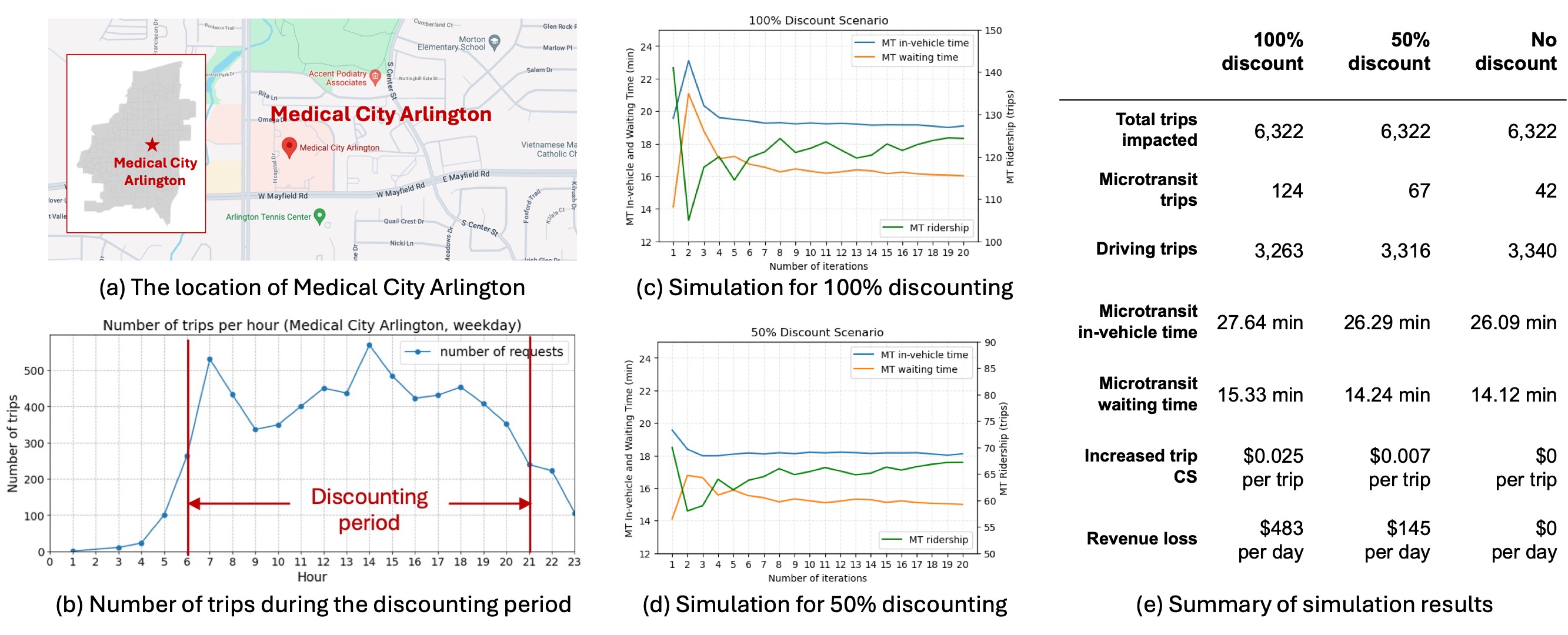
Microtransit Revenue Management for Arlington Via
We propose a nested nonparametric model for joint travel mode and ride pass subscription choice, estimated using marginal subscription data and synthetic populations. We apply our methodology to a case study in Arlington, TX, using synthetic data from Replica Inc. and microtransit data from Via.
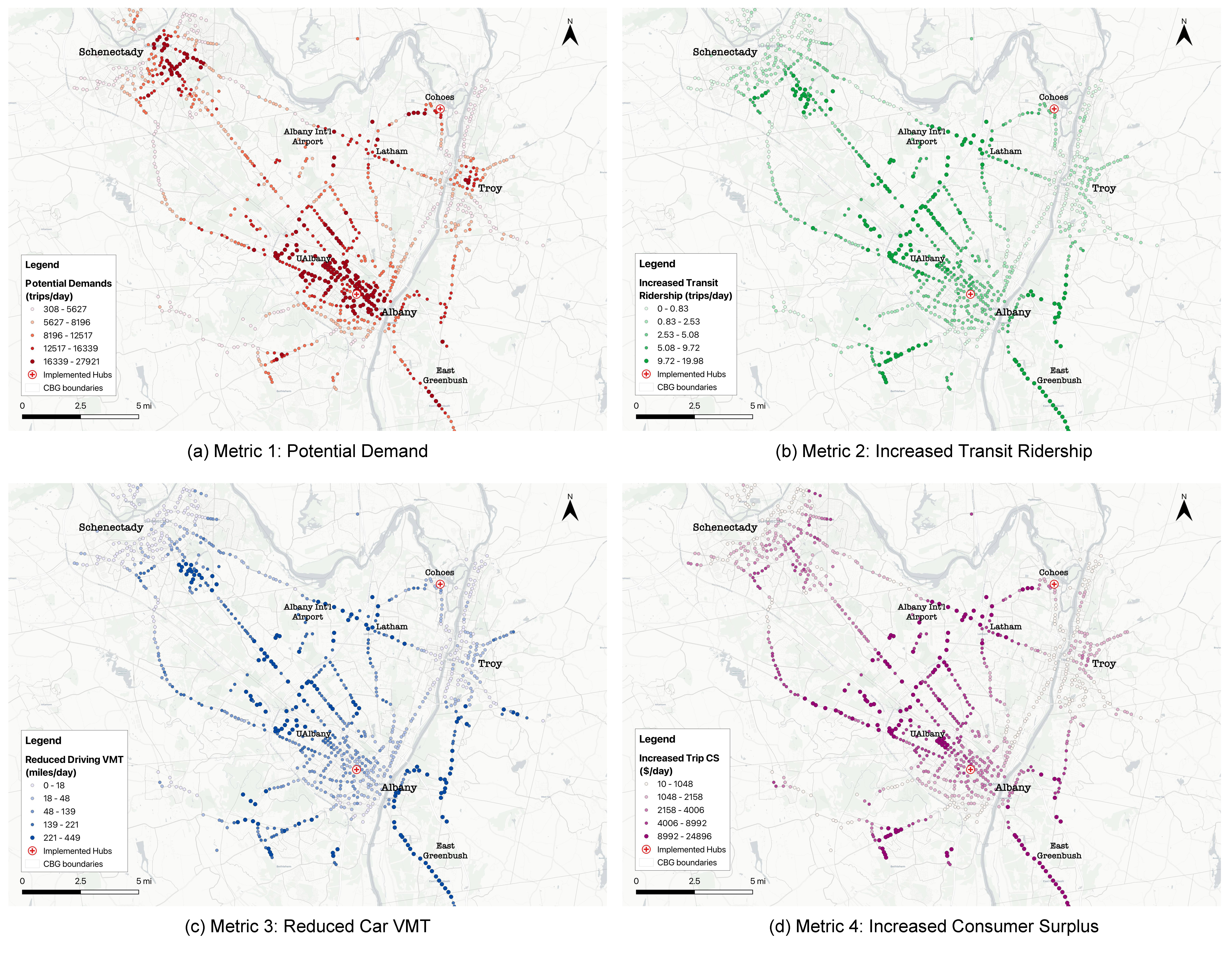
Mobility Hub Location Selection
We combine data from a survey conducted by the Capital District Transportation Authority (CDTA) with a mode choice model estimated using Replica Inc.’s synthetic data. The framework is applied to the evaluation of potential hub candidates in the Albany-Schenectady-Troy metropolitan area.